Taking too much vitamin C usually isn’t harmful, but it can sometimes lead to bothersome side effects. People with hemochromatosis should be extra careful because too much vitamin C might make their symptoms worse and increase the risk of tissue damage.
During cold and flu season, many supplement companies push products claiming to help you avoid getting sick. Vitamin C, a known and readily available antioxidant, is frequently promoted for its supposed health benefits.
Also known as ascorbic acid, vitamin C is a water-soluble nutrient found naturally in many fruits and vegetables. To ensure they’re getting enough, some people turn to supplements, but there are concerns about taking too much by accident.
Although taking too much vitamin C can cause unpleasant effects, serious overdoses are rare. Knowing the right amount to take is essential for good health.
Vitamin C acts as an antioxidant, protecting your body from free radicals that can damage your cells. It’s known as a virus-fighting vitamin because it helps support the body’s defense against illnesses. It also helps with iron absorption, which is crucial for the body’s functions and growth. Not getting enough vitamin C can lead to scurvy, which is potentially serious.
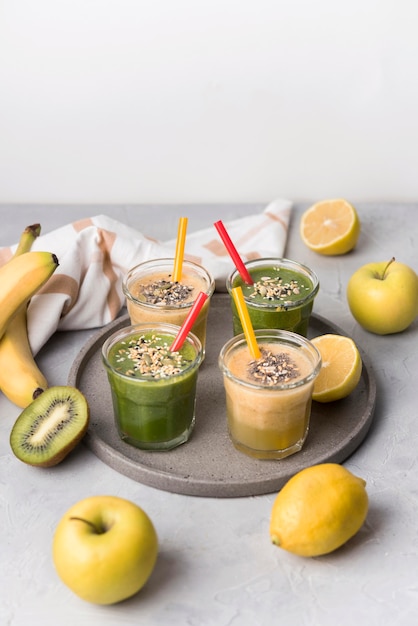
While oranges are famous for containing a lot of vitamin C, other fruits and vegetables like bell peppers, broccoli, cantaloupe, grapefruit, kiwi, potatoes, strawberries, and tomatoes are also great sources. If you eat plenty of these, you might not even need a supplement—just one serving of these foods could be enough to meet your daily needs.
The National Institutes of Health suggests a daily vitamin C intake of 70 mg for adult women and 90 mg for adult men. Pregnant and nursing women might need more, so it’s best to talk to a doctor about personal nutritional needs. The maximum amount for adults is 2,000 mg per day.
Going over this limit isn’t likely to be life-threatening, but it might cause issues like stomach pain, cramps, diarrhea, headaches, nausea that might lead to vomiting, and sleeping problems. People with hemochromatosis, a condition where too much iron is stored, need to be careful, as they could risk tissue damage. Vitamin C supplements could also interfere with certain medications, especially heart disease and cancer treatments, so it’s wise to consult a doctor first.
The pros of vitamin C include its antioxidant properties, support for collagen synthesis, boosting the immune system, and aiding in wound healing. On the downside, too much can cause digestive issues, kidney stones, interfere with medications, and only has limited effect in preventing colds.
Vitamin C mainly serves as an antioxidant important for collagen formation, wound healing, iron absorption, and immune function. It’s usually obtained from fruits and vegetables or as a supplement. Carvedilol, on the other hand, is used for heart conditions, helping relax blood vessels and reduce the heart’s workload.
Instead of relying heavily on vitamin C supplements, which don’t prevent colds or flu according to scientific evidence, it’s better to focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables. Taking everyday health measures like getting enough sleep, regular exercise, eating nutritious foods, and limiting caffeine and alcohol is more effective for maintaining good health and keeping viruses at bay.
The common cold is a frequent ailment, and there’s been a lot of talk about vitamin C possibly helping with it. Linus Pauling once promoted high doses of vitamin C as a treatment for colds, but research hasn’t really backed up these claims. Studies show that taking regular vitamin C supplements might slightly ease cold symptoms and shorten how long they last, but doesn’t significantly reduce the chances of catching one.
Vitamin C is crucial during infections because it’s concentrated in immune cells and gets used up quickly. A deficiency can weaken the immune system, so ensuring enough vitamin C when you’re under the weather is helpful.
Overall, vitamin C plays a key role in health as an antioxidant and in maintaining strong tissues. While severe vitamin C deficiency is rare today, it’s important to get enough, especially when you’re sick, to support the immune system. A balanced diet rich in vitamin C is a great way to help protect your health.